Definition
A region is an independent set of states and transitions, with its own active state. A state machine (or a composite state) is made of one or more regions. Two or more regions are said to be orthogonal when they belong to the same composite state (or to the state machine).
Orthogonal regions are separated by dashed lines:
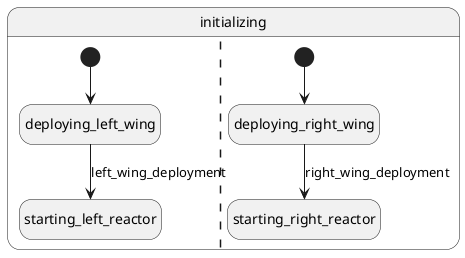
Orthogonal regions run in parallel. In the example above, the state machine initializes both wings separately, without waiting for one wing to be in place before deploying the other.
When to Use Orthogonal Regions
You use orthogonal regions to split the behavior of a system or subsystem into as many independent parts.
How to Define Orthogonal Regions with Maki
A state machine (or a composite state) is made of one or more regions. To add a region to a state machine (or to a composite state), you just have to add a transition table to the list given to maki::machine_conf::transition_tables() (or to maki::state_mold::transition_tables()).
Whenever the state machine (or the composite state) processes an event, it iterates over its regions in the order in which their transition tables are listed.
- Important
- When the same state mold is referenced in several transition tables (i.e. in several regions, orthogonal or not), it's used to make several, independent maki::state objects.